Western diets pose a larger threat of inflammatory bowel illness (IBD) and colorectal most cancers, in accordance with a milestone overview of what individuals eat around the globe.
The examine of six prevalent diets has examined how what we eat impacts our intestine microbiome—the group of microorganisms that stay in our intestines—and the way the shifting stability of its composition influences our general well being. The overview was carried out by APC Microbiome Eire (APC), an SFI Analysis Centre at College School Cork (UCC), and Teagasc.
The overview is published in Nature Opinions Microbiology and titled “The interaction between eating regimen and the intestine microbiome: implications for well being and illness.”
The examine, led by Prof. Catherine Stanton—an APC PI and senior principal analysis officer at Teagasc, examined Mediterranean, high-fiber, plant-based, high-protein, ketogenic, and Western diets.
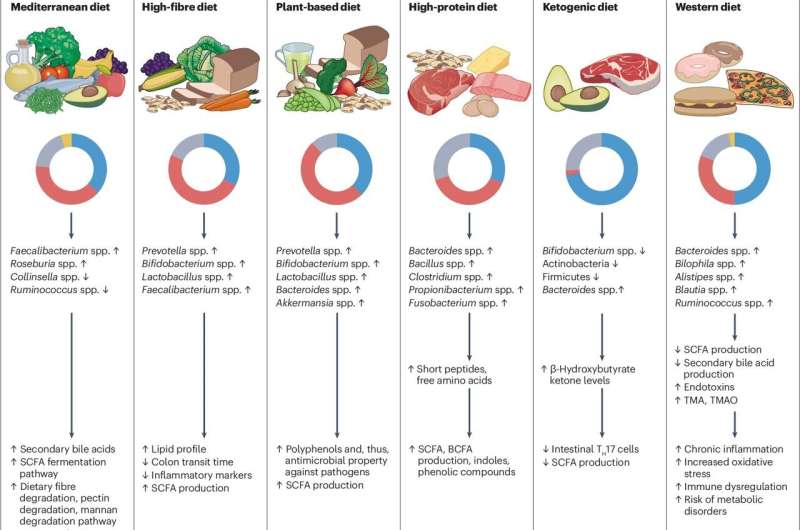
The excellent overview reveals how completely different diets considerably alter the composition and performance of the intestine microbiome, highlighting the manufacturing of important molecules produced throughout metabolism reminiscent of short-chain fatty acids.
It underscores the detrimental results of the Western eating regimen, characterised by excessive fats and sugar consumption, in comparison with the advantages of diets wealthy in plant-based and high-fiber meals.
Against this, it finds {that a} Mediterranean eating regimen, excessive in fruits, greens, is efficient in managing situations reminiscent of heart problems, IBD, and sort 2 diabetes.
Prof. Stanton stated, “Our overview highlights the profound affect of various diets on the intestine microbiome. This understanding is essential for creating dietary suggestions that promote well being and stop illness. It is fascinating to see how dietary selections can affect the stability of microorganisms in our intestine and their metabolic capabilities.”
The overview provides priceless insights for the meals trade and well being care professionals, guiding them in making knowledgeable selections about eating regimen and well being. The detailed evaluation of how completely different diets have an effect on the microbiome gives a basis for creating focused dietary therapies and enhancing public well being outcomes.
Prof. Paul Ross, Director of APC Microbiome Eire, and co-director of UCC Futures Microbiome and Well being added, “This overview is a major milestone in microbiome analysis. It gives an in depth take a look at how dietary patterns form the intestine microbiome and underscores the potential for diet-based interventions in scientific observe. It gives tangible information on how the microbiome is intrinsically related to creating well being advantages for society.”
The overview additionally emphasizes the necessity for exhaustive research to raised perceive the causal relationships between people, their eating regimen, and microorganisms. This understanding is significant for advancing precision vitamin and creating microbiome-based therapies tailor-made to particular person well being wants.
Extra info:
Fiona C. Ross et al, The interaction between eating regimen and the intestine microbiome: implications for well being and illness, Nature Opinions Microbiology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41579-024-01068-4
Supplied by
Teagasc
Quotation:
Western diets pose larger threat of most cancers and inflammatory bowel illness, examine finds (2024, July 18)
retrieved 21 July 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-07-western-diets-pose-greater-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.