New work has disclosed vital findings on the survival of the Legionella pneumophila bacterium in hospital water techniques. Just lately published within the journal Science of The Whole Atmosphere, the research suggests changes to regulate insurance policies to successfully fight legionellosis.
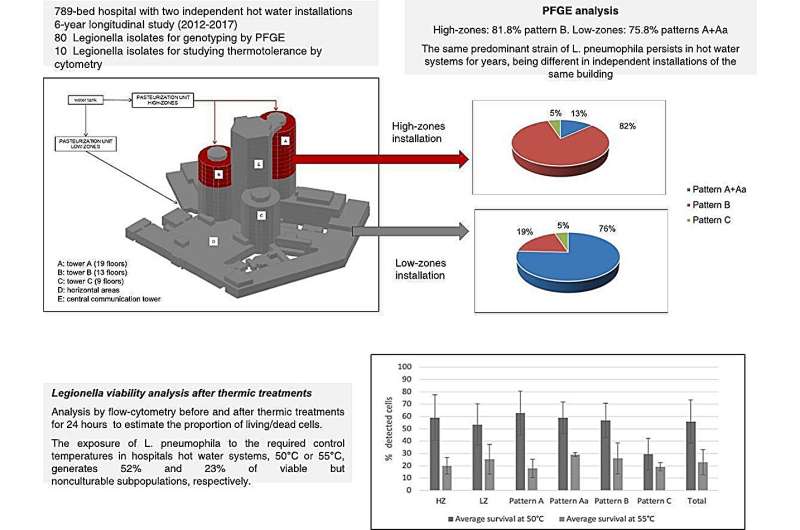
The research examined 80 isolates of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 6 from two unbiased sizzling water techniques in a hospital, highlighting the genotypic variability and thermotolerance of the strains. By utilizing stream cytometry to evaluate membrane integrity after exposing the micro organism to temperatures of fifty°C, 55°C, and 60°C for twenty-four hours, the group discovered {that a} vital share of micro organism confirmed no progress on plate cultures, however remained in a viable however non-culturable (VBNC) state.
Particularly, 52% of the micro organism at 50°C and 23% at 55°C retained their membrane integrity, whereas lower than 5% did so at 60°C. These findings underscore the limitation of the plate tradition technique for detecting Legionella below thermal stress circumstances.
The analysis group contains the Scientific and Environmental Infectious Illnesses Research Group (CEID) at Germans Trias i Pujol Analysis Institute (IGTP), led by Dr. Laura Gavaldà from the Bellvitge College Hospital, in collaboration with Institut Català d’Oncologia and Barcelona Public Well being Company.
Noemí Párraga, the primary writer of the research, emphasizes, “The plate tradition method for Legionella management, required by Spanish laws, underestimates the presence of this micro organism below stress elements, as it could stay in a viable however non-culturable state. This state will be reversed, recovering the microorganism’s infective functionality.”
This research suggests the potential for enhancing detection strategies to make sure protected hospital environments, acknowledging that Legionella can face up to regulatory temperatures and stay in a viable however non-culturable state. It’s advisable to contemplate this subpopulation in assessments, because it has the potential to grow to be infectious.
“Rising the temperature by 5˚C on the endpoints of sizzling water circuits might considerably cut back instances of legionellosis, particularly in facilities with a excessive presence of at-risk people,” factors out Dr. Gavaldà.
In 2022, the brand new Royal Decree 487/2022 was revealed in Spain, establishing the sanitary necessities for the prevention and management of legionellosis. This doc units out a sequence of measures for the prevention and management of Legionella in water installations. One of many outlined measures is the temperature in cold and warm water circuits. A minimal temperature of 60°C is established in accumulators and 50°C on the endpoints (faucets and showers) and on the return. The minimal required by the present royal decree are the microbiological controls by means of plate tradition.
Dr. Laura Gavaldà was a specialist within the Preventive Medication and Hospital Hygiene Service at Bellvitge Hospital on the time of the research. She is at present the pinnacle of the Tuberculosis Prevention and Management Service and Particular Applications on the Public Well being Company of Catalonia.
Extra data:
Noemí Párraga-Niño et al, Persistence of viable however nonculturable Legionella pneumophila state in hospital water techniques: A hidden enemy?, Science of The Whole Atmosphere (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172410
Supplied by
Germans Trias i Pujol Analysis Institute
Quotation:
Research reveals have to evaluate temperature management measures in hospitals to handle Legionella (2024, Could 10)
retrieved 11 Could 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-05-reveals-temperature-hospitals-legionella.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.