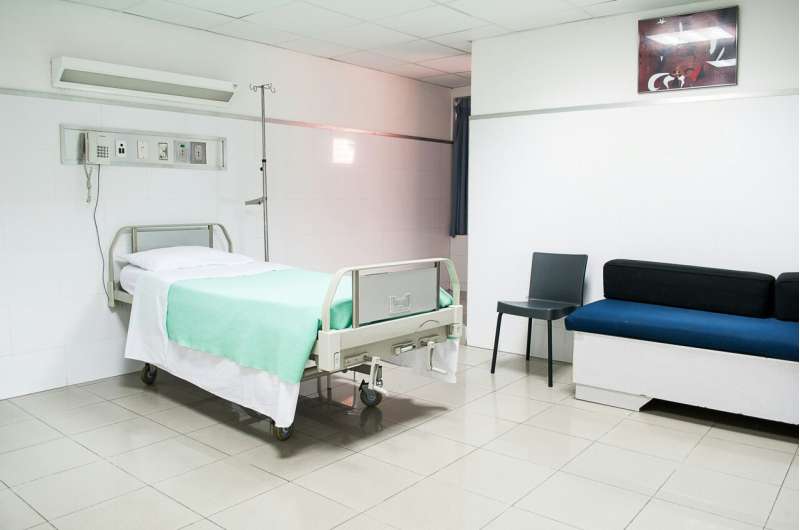
Cleansing shared medical tools at the very least as soon as a day—even with a disinfectant wipe—can considerably scale back infections in hospitals and presumably save lives, new analysis reveals.
The discovering is predicated on outcomes from the CLEEN examine, a randomized management trial led by Professor Brett Mitchell from Avondale College in a hospital on the Central Coast of New South Wales, with colleagues together with fellow chief-investigator and Monash College Professor Philip Russo.
Published in The Lancet Infectious Ailments, the examine launched an intervention that consisted of further cleansing, training on strategies and an audit of and suggestions on cleanliness.
Devoted cleaners, fairly than well being care staff normally accountable for cleansing, accomplished three further hours of cleansing every day on shared tools akin to commodes, drip stands and strolling aids.
To measure cleanliness, the researchers positioned fluorescent marker gel dots on the floor of the tools. When the dots dried, they turned seen solely underneath particular mild and resisted dry abrasion, which meant they may very well be eliminated solely by a radical clear.
“We recognized comparatively low ranges of cleansing thoroughness throughout the management part,” the researchers wrote, which instructed “routine cleansing is both not carried out or is ineffectively carried out.”
Earlier than the intervention, the hospital eliminated about 25% of the dots. After the intervention, it was 65%—a 35% discount in all well being care-associated infections.
The discovering is necessary as a result of 165,000 infections—essentially the most complete estimate in many years in line with earlier analysis by Professor Mitchell and different colleagues—happen in Australian hospitals annually. With infections not solely costing cash however taking lives, the burden is critical.
Professor Mitchell mentioned the findings supported extra—not much less—cleansing in hospitals. He mentioned earlier than the CLEEN examine, there have been about 100 extra infections earlier than the intervention. “A proportion of those would have had main problems ensuing from their an infection, together with dying,” he mentioned.
Professor Russo, director of analysis at Monash Nursing and Midwifery, mentioned the examine demonstrated the essential function of devoted cleaners. “An infection prevention depends on a number of interventions, not only one. We now have robust proof that cleansing can save lives,” he mentioned.
Regardless of the related enhance in morbidity, mortality and antimicrobial resistance—to not point out size of keep—methods to forestall well being care-acquired infections are knowledgeable by low-quality proof.
Professor Mitchell is conscious of solely six high-quality randomized management trials round cleansing and well being care-acquired infections, “and we have printed two.”
He mentioned there have been so few as a result of management of things that would contaminate outcomes was troublesome and the variety of contributors wanted to construct confidence was giant.
Trial coordinator Dr. Kate Browne, from Avondale College, mentioned it was a worthy funding. “Sturdy, evidence-based trials are the muse of recent medication,” Dr. Browne mentioned. “The information generated helps inform scientific insurance policies and tips that in the end enhance the standard of affected person care.”
Extra data:
Katrina Browne et al, Investigating the impact of enhanced cleansing and disinfection of shared medical tools on health-care-associated infections in Australia (CLEEN): a stepped-wedge, cluster randomised, managed trial, The Lancet Infectious Ailments (2024). DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00399-2
Quotation:
Intervention for cleansing shared well being care tools may considerably scale back well being care–related infections (2024, August 16)
retrieved 16 August 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-08-intervention-health-equipment-significantly-careassociated.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.