New findings from one of many few research reporting long-term well being outcomes for kids with extreme malnutrition have been published on February 15, 2024, in The Lancet Youngster and Adolescent Well being. The paper is titled “Lengthy-term outcomes after extreme childhood malnutrition in adolescents in Malawi (LOSCM): a potential observational cohort research.”
This potential cohort research adopted a bunch of Malawian kids for 15 years after their therapy in hospital for extreme childhood malnutrition. The research compares the well being outcomes of this group (now of their teenage and younger grownup years) to their siblings and friends of the same age from their communities who didn’t have extreme malnutrition as kids. Researchers name for motion to save lots of lives short-term, and make sure the long-term well being, improvement and well-being of youngsters who’ve survived episodes of early-life malnutrition.
Only a few different research have been in a position to observe a susceptible group comparable to this over such a very long time interval. With malnutrition presently within the information in quite a few international locations and the subject receiving vital consideration following the July 2023 release of recent World Well being Group (WHO) Pointers on malnutrition, the challenge is very well timed and essential.
The researchers, led by the College of Liverpool and dealing in partnership with quite a lot of collaborators together with the London Faculty of Hygiene & Tropical Medication, the Malawi-Liverpool Wellcome Belief Scientific Analysis Program and the Kamuzu College of Well being Sciences, Malawi, adopted up and investigated the well being outcomes of 168 adolescents with earlier extreme childhood malnutrition, alongside 123 siblings and 89 adolescents from the group with out earlier extreme malnutrition.
Findings
Total, the researchers summarized {that a} very excessive variety of these with extreme childhood malnutrition died within the years after discharge from care, and survivors had persistent unfavorable results of decrease peak and doable decrease energy in comparison with these with out earlier extreme malnutrition. Nonetheless, survivors exhibited “catch-up” development in childhood and past, which offers optimism for ongoing restoration of peak deficits after therapy.
The researchers recommend these findings spotlight the significance of supporting the diet, well being, and well-being of these with extreme childhood malnutrition after discharge from care, and the necessity to handle antagonistic life circumstances all through early childhood and adolescence.
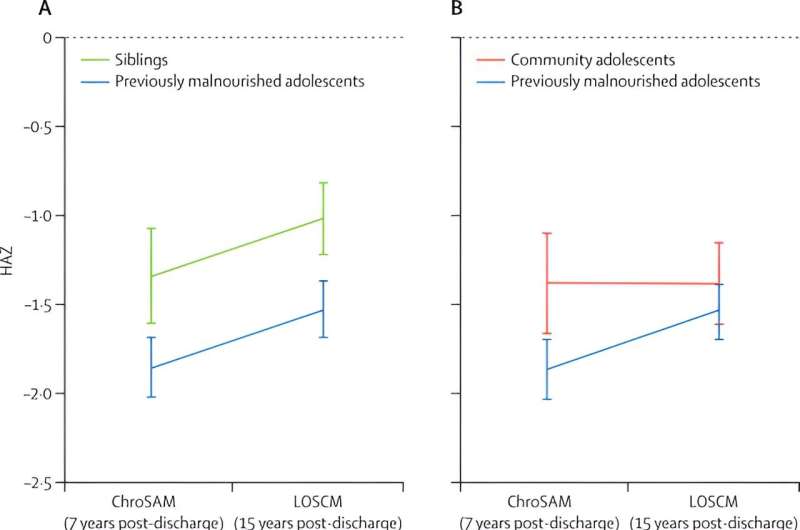
The London Faculty of Hygiene & Tropical Medication’s Dr. Marko Kerac stated, “Whereas we have been completely happy to see that the well being and development of our survivors of kid malnutrition from 2006/7 appears to be catching up with sibling and group friends, it’s critical to see these ends in context.
“Over 1,000 kids have been initially admitted to our extreme malnutrition therapy program. Many died in-program and within the months and years after. It’s thus significantly tragic that the world has not moved ahead a lot since that meals disaster 15 years in the past. With local weather disaster and battle, there are thousands and thousands of youngsters who even at this time undergo from starvation and malnutrition.
“Pressing motion is required, not simply to save lots of lives short-term, however to make sure the long-term well being, improvement and well-being of any survivors. Prevention and therapy of kid malnutrition must not ever be seen as a value however as an funding for the way forward for people, societies and full international locations.”
Lead researcher, Dr. Amir Kirolos from the College of Liverpool and Malawi-Liverpool-Wellcome Belief stated, “Prevention, early identification, and therapy of extreme childhood malnutrition saves lives. Our research exhibits the significance of addressing different antagonistic components alongside therapy for extreme malnutrition. Poverty, starvation, and residing with HIV have been widespread in our research and have an effect on too many kids and youngsters in Malawi and worldwide.
“We’d like additional analysis and funding to deal with these antagonistic components and all types of baby malnutrition. This may permit affected kids to not solely survive, however thrive, reaching their full potential within the long-term.”
Subsequent steps
Though this cohort didn’t discover sturdy proof of impaired cognition or greater cardiometabolic illness threat, the group continues to be younger and the researchers suggest that additional analysis in Malawi and throughout different settings is required to raised perceive long-term well being dangers as they develop into later maturity.
Additional investigation and funding into enhancing dwelling and life circumstances of these with adversity is required to enhance the long-term well being outcomes of thousands and thousands of youngsters worldwide presently affected by malnutrition.
Extra data:
Amir Kirolos et al, Lengthy-term outcomes after extreme childhood malnutrition in adolescents in Malawi (LOSCM): a potential observational cohort research, The Lancet Youngster & Adolescent Well being (2024). DOI: 10.1016/S2352-4642(23)00339-5
Quotation:
Researchers examine long-term outcomes after extreme childhood malnutrition (2024, February 16)
retrieved 16 February 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-02-term-outcomes-severe-childhood-malnutrition.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.









