Over the past 20 years, the life sciences have come to understand that every one dwelling beings—from the best animal and plant organisms to people—reside in shut affiliation with a mess of microorganisms. Along with the multicellular host organism, these symbiotic micro organism, viruses and fungi, which colonize on and of their tissues and type the so-called microbiome, represent a primarily helpful neighborhood within the type of a metaorganism.
Many life processes, together with the well being and illness of the organism as an entire, can solely be understood within the context of this practical co-operation between the host organism and microorganisms, for instance within the absorption of vitamins, immune perform or neuronal processes.
In current a long time, nevertheless, the approach to life in industrialized societies has led to a gradual depletion of variety of the human microbiome and this has contributed to the event of so-called environmental illnesses, for instance inflammatory bowel illnesses, sort 2 diabetes or neurodegenerative problems.
At Kiel College, host-microbe interactions and their results on well being and illness are being investigated intimately within the Collaborative Analysis Middle (CRC) 1182 “Origin and Operate of Metaorganisms.”
A gaggle of scientists concerned within the “People and the Microbiome” analysis program on the Canadian Institute for Superior Analysis (CIFAR) in Toronto have revealed a perspective paper, in Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences, proposing a brand new dimension for the examine of the human microbiome and a paradigm shift in city and constructing planning.
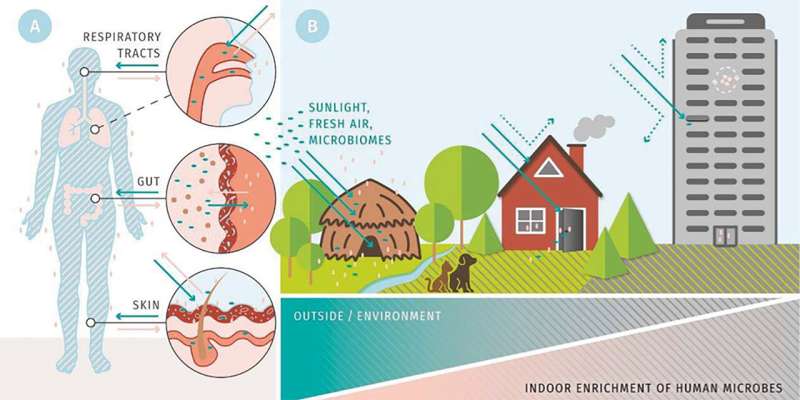
They talk about the affect of the so-called constructed setting on the composition and variety of the microbiome. They put ahead the speculation that trendy buildings have a big affect on human microbial colonization, relying on their nature and diploma of defending from the setting, and that this side needs to be taken into consideration in future structure when it comes to wholesome and microbiome-friendly constructing situations.
The researchers, embody Professor Beatriz Colomina from Columbia College, Professor Brendan Bohannan from the College of Oregon, Professor Margaret McFall-Ngai from the California Institute of Expertise and CRC 1182 board member and Kiel Life Science Spokesperson Professor Thomas Bosch from Kiel College.
Buildings interrupt contact with microorganisms from the setting
The human quest for shelter and safety from the weather is as previous as mankind itself, for hundreds of years individuals everywhere in the world have been creating and growing all kinds of dwellings proper as much as the structure of right this moment; within the close to future greater than two thirds of the world’s inhabitants will reside in cities. General, the city life-style, together with many different elements, has ensured that life expectancy and high quality of life have improved considerably for almost all of humanity.
“Nonetheless, buildings as such and the triumph of city dwelling have additionally produced unfavorable results by shielding individuals to a better or lesser extent from contact with their microbial setting. The extent of those presumably unfavorable penalties for the composition and variety of the human microbiome can hardly be estimated as but,” explains CIFAR Fellow Bosch.
The researchers see the primary motive for this in the truth that our trendy life in constructed environments more and more prevents contact with the multitude of microbes within the pure setting. As well as, buildings themselves have to be seen as advanced natural programs within the sense of numerous interdependent microbial communities, which additionally have an effect on the human metaorganism.
Taken collectively, this has unfavorable penalties, for instance by creating new niches for illness hosts and vectors in buildings, concentrating waste and poisonous substances or lowering air flow and the entry of daylight.
All of this in flip influences the human microbiome in quite a lot of methods: For instance, the constructed setting creates novel reservoirs of dangerous microbes tailored to people, reduces the publicity of people to helpful microbes, or alters human habits to inhibit pure and helpful transmission of microorganisms between individuals.
“If human well being is outlined as being depending on a big variety of the microbiome, then a big proportion of right this moment’s buildings have to be thought-about as not conducive to well being when it comes to development and design, supplies or sort of use—as a result of in sum, their results seem to cut back microbial variety, which may result in poorer total well being of the occupants,” emphasizes Bosch.
Future structure ought to restore permeability for microorganisms
Since their invention, buildings have usually unintentionally brought about well being issues, although individuals have all the time tried to make them more healthy and safer. The examine of the hyperlinks between structure and well being is due to this fact not at all new, and a vital query right this moment is: how can buildings be designed for higher well being and constructed in such a means {that a} advanced and various microbiome can survive?
“By wanting on the impression of constructing traits on the human microbiome, we’re including an entire new and necessary dimension to this advanced. Our city lifestyle ignores the truth that the physique has tailored to its setting and its microbes over hundreds of years and that it is just match and wholesome in touch with these accomplice organisms,” says Bosch.
“Provided that we settle for this multi-organismic complexity will we arrive at a deep understanding of well being and thus an understanding of frequent illnesses. The completely revolutionary view of dwelling organisms and microbes as a practical unit can even shift the boundaries of city planning sooner or later. We provide modern scientific and utilized views for the event of a future, microbiome-friendly structure that may as soon as once more permit pure and wholesome human contact with microorganisms within the constructed setting.”
The prerequisite for that is that in future, buildings are developed with the extra objective of dosed and managed publicity of individuals to microorganisms specifically—and now not see them completely as a barrier to push back environmental influences, as was beforehand the case.
In line with the researchers, one purpose may due to this fact be to plan and assemble the constructed setting in future in such a means that the main target is just not on full isolation from the pure, microbial setting. Quite the opposite: buildings may be opened as much as nature once more and made extra nature-friendly.
This may be achieved, for instance, by utilizing much less poisonous constructing supplies and creating an total better structural permeability to exterior, notably microbial, influences.
“With this angle, we’re basically increasing our view of the human microbiome and establishing a direct hyperlink to the constructed setting by means of to trendy city planning. This ends in fascinating new approaches that take care of microbiome-friendly structure and development and should in future be mirrored in a considerably improved constructed setting that will likely be helpful to human well being,” says Bosch.
Extra data:
Thomas C. G. Bosch et al, The potential significance of the built-environment microbiome and its impression on human well being, Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2313971121
Quotation:
How buildings affect the microbiome and human well being (2024, April 26)
retrieved 26 April 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-04-microbiome-human-health.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.